Introduction
In today’s fast-paced healthcare environment, clinicians are increasingly expected to deliver timely, accurate, and patient-centered care. One of the most significant technological advancements supporting this shift is the emergence of point-of-care (POC) immunoassay analyzers. These compact, user-friendly diagnostic devices bring laboratory-grade testing capabilities directly to the bedside, clinic, emergency department, or even remote field settings. As demand for rapid diagnostics continues to rise, POC immunoassay analyzers have become essential tools across a wide range of clinical scenarios.
Definition
Point-of-care immunoassay analyzers are compact diagnostic devices that perform immunoassay tests – such as detecting specific proteins, hormones, or infectious disease markers – directly at or near the site of patient care. Using antibody-based reactions to identify target biomarkers, these analyzers deliver rapid, reliable results without the need for centralized laboratory equipment, supporting faster clinical decisions in settings like clinics, emergency rooms, and remote or resource-limited environments.
What Are Point-of-Care Immunoassay Analyzers?
Point-of-care immunoassay analyzers are devices designed to detect and quantify specific antigens, antibodies, hormones, or biomarkers in patient samples – typically blood, plasma, serum, urine, or saliva. They use immunoassay technology, which relies on the highly specific binding between an antigen and an antibody. Unlike traditional laboratory analyzers that require large instruments, multiple reagents, and trained lab personnel, POC immunoassay analyzers are portable, automated, and built for rapid turnaround times.
These systems are commonly used to test for:
- Cardiac biomarkers (e.g., troponin, BNP)
- Infectious diseases (e.g., influenza, COVID-19, strep)
- Hormonal levels (e.g., hCG for pregnancy)
- Inflammatory markers (e.g., CRP, procalcitonin)
- Coagulation markers (e.g., D-dimer)
- Metabolic indicators (e.g., HbA1c)
Because they provide results in minutes rather than hours, POC immunoassay analyzers allow clinicians to make faster decisions, improving patient outcomes and workflow efficiency.
How Do These Analyzers Work?
Although designs vary by manufacturer, most POC immunoassay analyzers follow similar underlying principles rooted in immunochemistry:
1. Sample Introduction
The patient sample—often a small drop of whole blood—is applied to a test cartridge or strip that contains the necessary reagents.
2. Antibody-Antigen Reaction
The target marker in the sample binds with labeled antibodies on the test cartridge. Labels may include fluorescent dyes, chemiluminescent agents, or enzymes.
3. Signal Detection
Once the immune reaction occurs, the analyzer measures the signal produced. Depending on the technology, this may be light emission, color changes, or fluorescence intensity.
4. Quantification and Reporting
The device uses built-in calibration curves and algorithms to translate signal strength into a quantitative result. Results are displayed within minutes and can often be transmitted electronically to electronic medical record (EMR) systems.
The marriage of microfluidics, advanced detection technologies, and smart connectivity has allowed POC immunoassay analyzers to deliver accuracy and precision comparable to centralized laboratories.
Key Advantages of Point-of-Care Immunoassay Analyzers
Rapid Turnaround Time:
Perhaps the greatest benefit is speed. Traditional laboratory immunoassays may take hours due to sample transport, batching, and lab workflows. In contrast, POC devices provide results in 5–20 minutes, enabling immediate interventions – critical in emergency medicine, cardiology, and infectious disease management.
Enhanced Clinical Decision-Making:
Faster results translate to faster decisions. For example:
- In chest-pain cases, a quick troponin test helps rule out myocardial infarction.
- Rapid CRP or procalcitonin results support antimicrobial stewardship efforts.
- Immediate pregnancy test results guide appropriate imaging and treatment decisions.
By reducing uncertainty, clinicians can tailor treatments more effectively.
Greater Accessibility:
POC immunoassay analyzers can be used in environments where traditional laboratory infrastructure is limited or unavailable:
- Rural clinics
- Ambulances and emergency response settings
- Field hospitals
- Urgent care centers
- Nursing homes
- Pharmacies
This democratization of diagnostic capability helps reduce disparities in healthcare access.
Improved Workflow Efficiency:
Reducing reliance on centralized labs decreases bottlenecks and enhances patient throughput. Clinics can complete patient visits in a single encounter without follow-up calls or delays waiting for external lab reports.
Reduced Patient Anxiety:
Fast results help minimize stress and support better patient engagement. In cases like suspected infection or cardiac events, waiting hours for lab results can be emotionally difficult.
Connectivity and Data Integration:
Modern POC systems can integrate with LIS/EMR platforms via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or wired connections, ensuring seamless data flow, reduced manual entry errors, and compliant documentation.
Applications in Modern Healthcare
Emergency Medicine:
Cardiac markers such as troponin and BNP are critical in triaging chest-pain patients. Rapid POC testing accelerates decisions about admission, discharge, or further imaging.
Primary Care and Family Medicine:
Routine tests like HbA1c, CRP, and infectious disease screens enable same-day diagnosis and treatment plans.
Pharmacy-Based Care:
As pharmacies expand clinical services, POC immunoassays help pharmacists deliver testing for flu, strep, COVID-19, and chronic disease monitoring.
Maternal and Women’s Health:
Rapid pregnancy hCG tests and other hormonal assays streamline care decisions in urgent and outpatient settings.
Infectious Disease Control:
During outbreaks, portable immunoassay analyzers support rapid testing and isolation decisions, improving public health response.
Remote and Resource-Limited Settings:
Their ability to operate with minimal infrastructure makes POC analyzers crucial for humanitarian missions, rural clinics, and mobile health units.
Limitations and Challenges
While powerful tools, POC immunoassay analyzers are not without drawbacks:
1. Limited Test Menus
Although expanding, POC test menus are smaller than those of full laboratory analyzers.
2. Higher Per-Test Cost
The convenience of rapid testing often comes with a higher cost per cartridge compared to bulk laboratory runs.
3. Operator Variability
Although designed for simplicity, errors can still occur if operators are not properly trained or quality-control procedures are not followed.
4. Calibration and Quality Control Requirements
Some devices require periodic calibration, external QC checks, and maintenance – factors that must be integrated into facility workflows.
5. Potential for Lower Sensitivity in Certain Assays
Although generally comparable, some POC tests may have lower sensitivity or specificity depending on assay design and sample type.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a POC Immunoassay Analyzer
Healthcare organizations evaluating POC analyzers should consider:
- Test menu relevance to their patient population
- Turnaround time relative to clinical needs
- Accuracy and precision compared to lab benchmarks
- Ease of use and training requirements
- Connectivity options (EMR/LIS integration)
- Cost per test and budget impacts
- Instrument durability and maintenance needs
- Regulatory compliance (CLIA-waived status, CE marking, etc.)
Selecting the right device depends on balancing clinical impact with operational and financial considerations.
The Future of Point-of-Care Immunoassay Technology
The field is evolving rapidly. Trends shaping the next generation of POC immunoassay analyzers include:
- Smaller and more portable devices with improved sensitivity
- Expanded biomarker panels, including multi-analyte cartridges
- Integration of AI and machine learning for enhanced result interpretation
- Cloud-based data analytics for population health management
- Greater involvement of POC diagnostics in home healthcare
As diagnostic technology continues to miniaturize and become more affordable, POC immunoassay analyzers will likely play an even stronger role in decentralized, personalized healthcare.
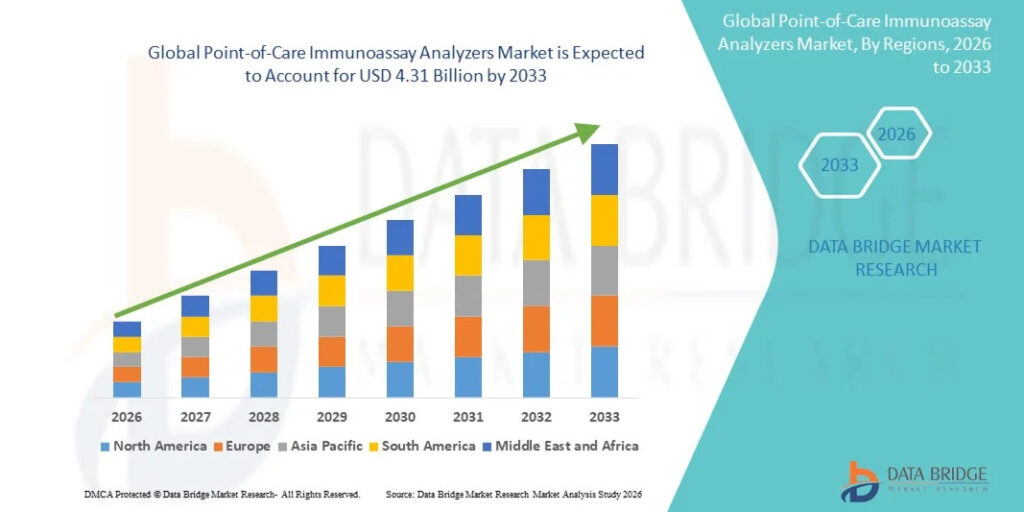
Growth Rate of Point-of-Care Immunoassay Analyzers Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the point-of-care immunoassay analyzers market was estimated to be worth USD 1.78 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.70% to reach USD 4.31 billion by 2033.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-point-of-care-immunoassay-analyzers-market
Conclusion
Point-of-care immunoassay analyzers represent a major advancement in rapid diagnostics, offering accuracy, speed, and accessibility that align perfectly with the needs of modern healthcare systems. From emergency departments to rural clinics, these devices empower clinicians with immediate insights that improve patient outcomes and streamline workflows. As innovation continues to expand their capabilities, POC immunoassay analyzers will remain a cornerstone of efficient, patient-centered care.